For CBSE class XI Chemistry Case study based questions.
Dear teacher it is challenging to make cased study based question for students. here we are providing 14 CSB question of XI class chemistry. easily you can insert these questions in your question papers. Each CSB Question is of 4 marks. There are 4 question in each CSB.
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Spectrum is combination of radiations of different wavelengths. Visible spectrum is continuous spectrum. Atomic spectrum (line spectrum) is discontinuous spectrum. It can be absorption or emission spectrum when energy is supplied to electrons, these get excited to higher energy levels. When they come back to lower energy level, they radiate energy in form of bright spectral lines separated by dark bands. Each element has its unique spectrum by which it can be identified.
(a) In Lyman series electron jump from which energy level to which energy level?
(b) To which region of spectrum Balmar series belong?
(c) Calculate mass of 1 mole of electrons. (me = 9.1 × 10–31 kg)
Or
(c) Calculate charge on 1 mole of electrons (e = 1.602 × 10–19 C)
Answer (a) Electrons jumps from 2, 3, 4, 5 …, to 1st energy level.
(b) Visible region
(c) Mass of 1 mole of electrons = 9.1 × 10–31 kg × 6.022 × 1023 = 5.48 × 10–7 kg
Or
(c) Charge on 1 mole of electron = 1.602 × 10–19 × 6.022 × 1023 = 96487 C
2. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Orbitals are regions or space where there is maximum probability of finding electrons. Orbitals are filled with electrons in increasing order of energy. Each degenerate orbitals is first singly filled, then pairing of electrons takes place. Quantum number ‘n’ determines energy of electron, ‘l’ determine shape of orbital and angular momentum, ‘ml’ determines magnetic orientation and ‘ms’ determines spin of electrons. Magnetic moment depends on number of unpaired electrons.
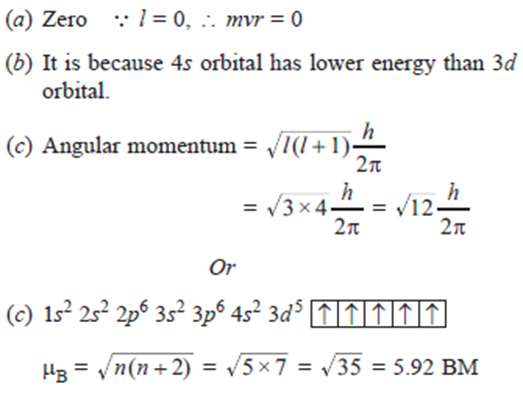
(a) What is angular momentum of 2s orbital?
(b) Why is 4s orbital filled before 3d orbital?
(c) Calculate angular momentum of electron in f-orbital.
Or
(c) Calculate magnetic moment of Mn2+ (25).
3. Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
Modern periodic table arranges the elements in the increasing order of atomic number. It has 18 groups and 7 periods. Atomic numbers are consecutive in a period and increases in group in a pattern. Elements are divided into four blocks, s-block, p-block, d-block and f-block based on their electronic configuration. 78% of elements are metals, about 20 elements are non-metals and few elements like B, Si, Ge, As are metalloids. Metallic character increases down the group but decreases along the period from left to right. The physical and chemical properties vary periodically with their atomic numbers. Periodic trends are observed in atomic size, ionisation enthalpies, electron gain enthalpies, electronegativity and valence. Oxides of metals are basic, some are amphoteric. Non-metals form acidic oxides, some form neutral oxides. s-block elements are soft, highly reactive, do not show variable oxidation states. p-block elements are metals, non-metals as well as metalloids, show variable oxidation states, exist as solids, liquids and gases. d-block elements are metals, form coloured ions, show variable oxidation states, have high melting and boiling points. Lanthanoids and actinoids are f-block elements, form coloured ions. All actinoids are radioactive.
(a) What are representative elements?
(b) Which of the following belong to d-block but are not transition elements? Zn, Cd, Hg, Ag.
(c) (i) What is difference between oxidation states of p-block and d-block elements?
(ii) Which group elements are most electropositive and most electronegative respectively?
Or
(c) Which type of compound is formed by Group 14 elements in 3rd period and what is the formula of its chloride and its oxide?
Answer- (a) s and p block elements are representative elements.
(b) Zn, Cd, Hg
(c) (i) In p-block elements oxidation states differ by 2 and lower oxidation state is more stable where as in d-block, oxidation state differ by 1 and mostly higher oxidation state is more stable.
(ii) Group 1 and Group 17 respectively.
Or
(c) The nature of bonding in group 14 elements is covalent bonding. The formula of its chloride is XCl4 and formula of oxide is XO2.
More Questions You can download from here-
